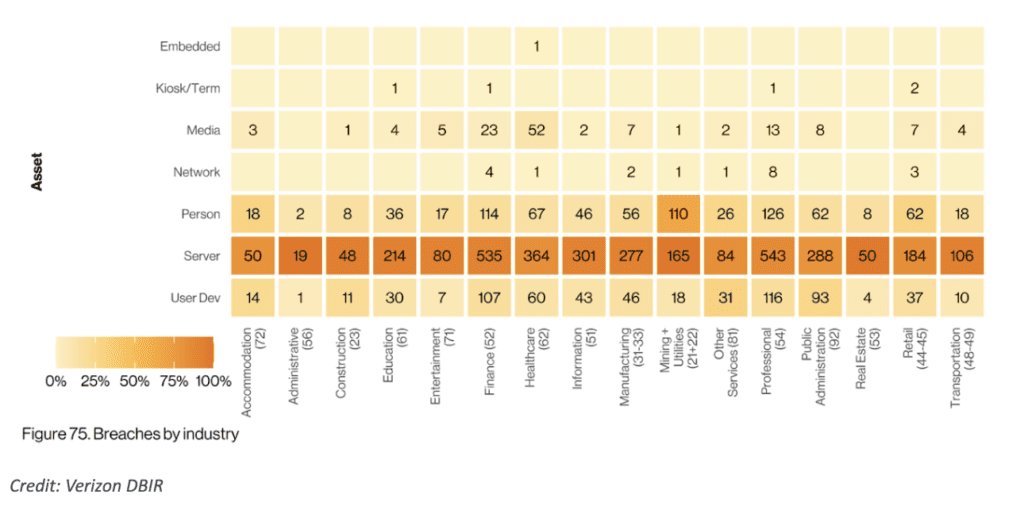
The Verizon 2022 DBIR report provides valuable insights into the state of data breaches and cybersecurity across all involved industries. By examining the report’s findings, we can better understand the unique challenges and vulnerabilities faced by different sectors. Let us delve into the key takeaways for each industry. To name a few, the manufacturing, public, and finance sectors possess a few of the top rankings that are in constant battle with cybercrime.
With the aforementioned industries, here are the key takeaways into the manufacturing, public, and finance sectors:
1. MANUFACTURING
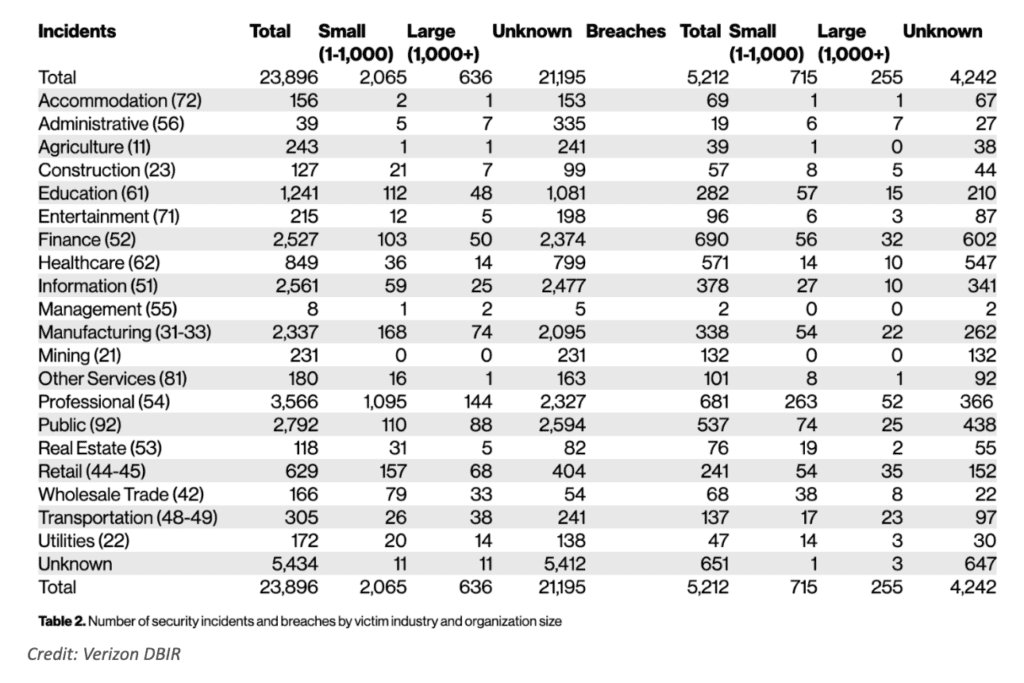
2,337 is the number of security incidents in 2022.
338 is the number of data breaches in 2022.
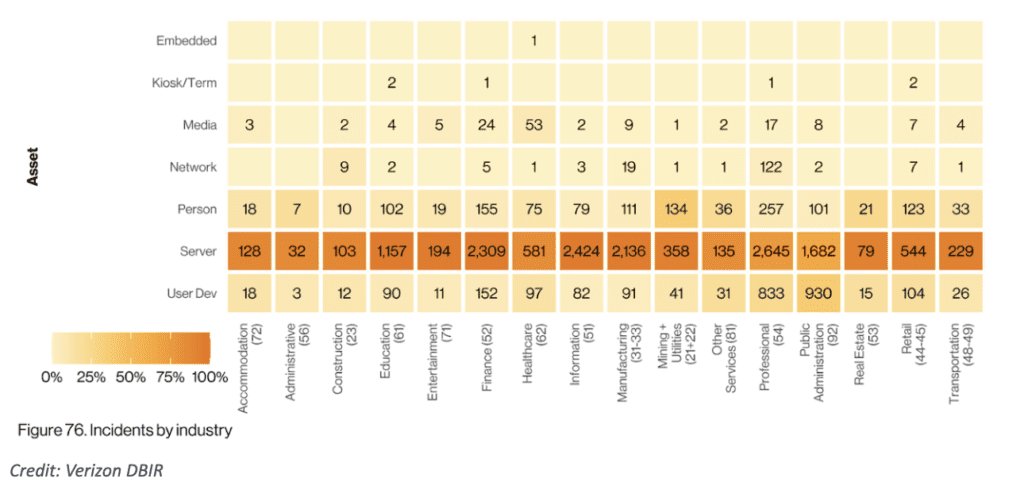
The DBIR reveals that manufacturing organizations experienced a substantial increase in phishing attacks and system intrusion incidents. These attacks aimed to compromise sensitive data, disrupt operations, or gain unwarranted access to intellectual property. With the rise of connected devices and the Internet of Things (IoT), manufacturing systems have become more vulnerable to exploitation. The report emphasizes the need for robust security measures, employee awareness training, and regular vulnerability assessments to safeguard manufacturing organizations against cyber threats.
2. PUBLIC
2,792 is the number of security incidents in 2022.
537 is the number of data breaches in 2022.
Moving on to the public sector, the attacked parties include government agencies and institutions. Verizon highlights that the most common attack vectors in this industry are malware and phishing. These attacks often aim to gain unauthorized access to sensitive government data, disrupt critical services, or perpetrate financial fraud. The report emphasizes the importance of implementing strong authentication measures, regular security assessments, and incident response plans to mitigate risks. Additionally, the report suggests that sharing threat intelligence among public sector entities can help strengthen the overall cybersecurity posture.
3. FINANCE
2,527 is the number of security incidents in 2022.
690 is the number of data breaches in 2022.
In the finance industry, security incidents and data breaches are of significant concern due to the potential financial and reputational impact. Financial institutions hold valuable customer information, including personally identifiable information and financial data. Cyberattacks targeting the finance sector aim to steal this sensitive information for financial gain or engage in fraudulent activities. The increasing sophistication of cyber threats, such as ransomware attacks and phishing scams, has contributed to the rising number of security incidents in the finance industry. Compliance requirements and the need for robust security measures to protect customer trust are key drivers behind the industry’s focus on cybersecurity.
What are the effects of these security incidents and data breaches?
First and foremost, a security incident and a data breach are related but distinct terms in the context of cybersecurity. Let’s clarify the difference between the two:
A security incident refers to any event that potentially compromises the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of information or systems. It encompasses a broad range of events, including unauthorized access attempts, malware infections, network intrusions, denial-of-service attacks, and social engineering incidents. Essentially, a security incident refers to any incident that poses a threat to the security of an organization’s information and technology infrastructure.
On the other hand, a data breach specifically refers to an incident where there is an unauthorized access, acquisition, or disclosure of sensitive or protected data. In a data breach, an attacker gains unauthorized access to data that they are not supposed to have, which can include personally identifiable information (PII), financial data, health records, or intellectual property. The breach could occur due to various reasons, such as a cyberattack, insider threat, or accidental exposure.
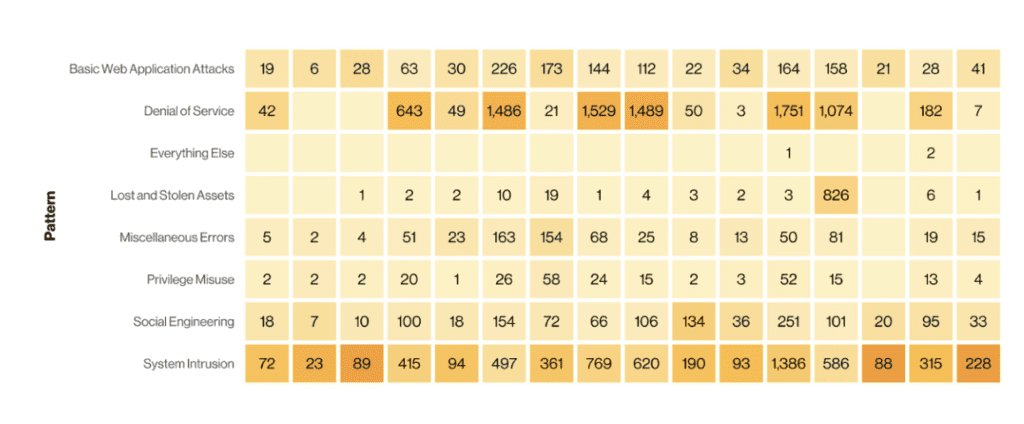
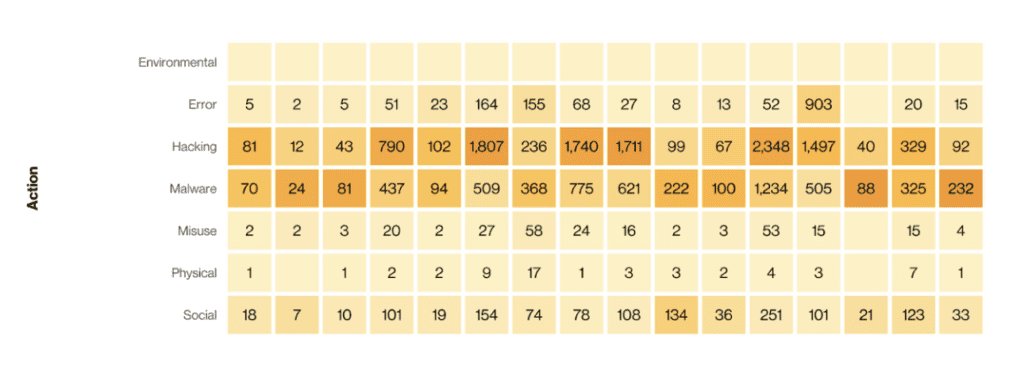
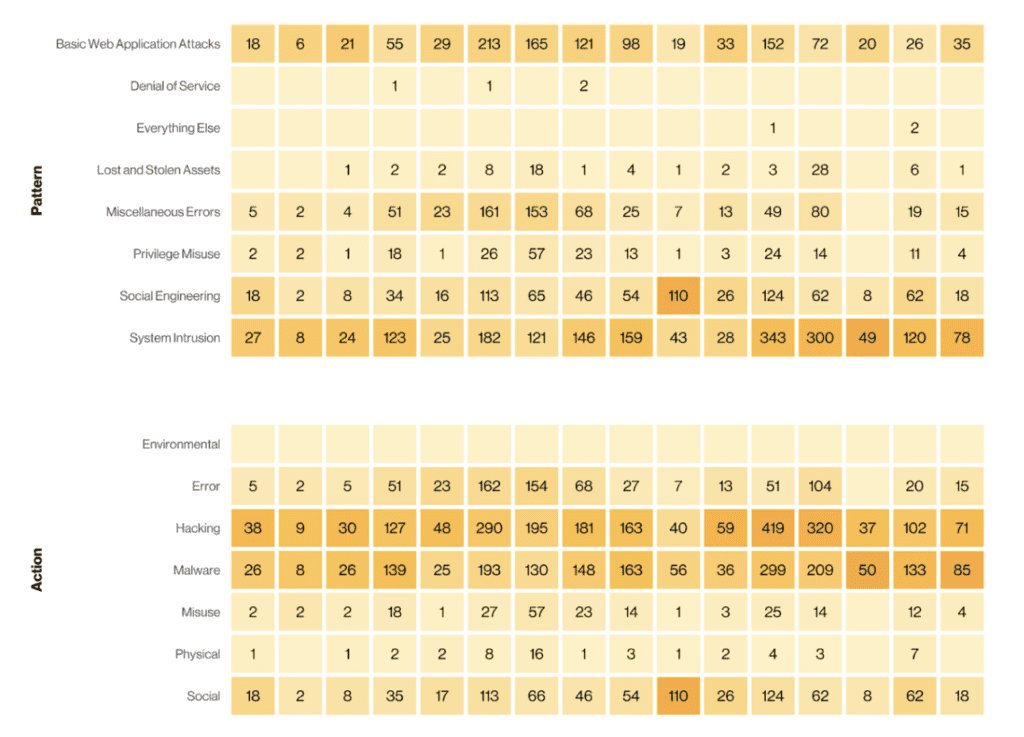
With that in mind, the most common types of security incidents in 2022 for businesses of all sizes and industries were system intrusion, social engineering, and basic web application attacks.
It is important to consider the broader implications these two can have on your business. Let’s explore the effects on both industries and businesses.
To understand the effects of security incidents such as system intrusion, social engineering, and basic web application attacks, as well as data breaches, on industries and businesses, it is important to consider the broader implications they can have. Let’s explore the effects on both industries and businesses.
In terms of industries, security incidents and data breaches can have several common effects. Firstly, they can result in financial losses due to the costs associated with incident response, remediation, legal fees, and potential regulatory fines. The reputational damage caused by such incidents can also lead to a loss of customer trust and loyalty, impacting the industry’s overall image. Additionally, industries may face regulatory scrutiny and increased compliance requirements following a breach, leading to additional costs and operational disruptions.
On the business level, the effects of security incidents and data breaches can be significant. A system intrusion, where unauthorized access to a network or computer system occurs, can compromise sensitive data, disrupt business operations, and lead to downtime, causing financial losses. Social engineering attacks, such as phishing or impersonation, can trick employees into revealing confidential information or granting unauthorized access, potentially leading to data breaches and financial fraud. Basic web application attacks, like SQL injection or cross-site scripting, can exploit vulnerabilities in websites or web applications, compromising customer data or facilitating unauthorized access.
Data breaches, in particular, have wide-ranging effects. Stolen customer information can be sold on the dark web, leading to identity theft and financial fraud for individuals. For businesses, data breaches can result in lawsuits, legal liabilities, and damage to their brand reputation. Moreover, intellectual property theft through data breaches can impact a company’s competitive advantage and innovation.
How can you protect your assets against cybercrime?
To protect your business assets, integrating risk pool concepts and captive insurance can be an effective strategy. Risk pooling involves sharing risks and resources among multiple entities, while captive insurance involves creating an in-house insurance company to cover specific risks. When combined with designated cyber security insurance coverage like privacy liability coverage and network business interruption coverage, businesses can enhance their overall risk management approach. Let’s explore how these elements can be utilized together.
By integrating risk pool concepts, businesses can join forces with other organizations to create a collective risk pool. This allows them to share the financial burden of potential losses, as well as benefit from the expertise and resources of the pool members. Risk pooling can help businesses access coverage for risks that may otherwise be costly or difficult to obtain individually, including cyber risks.
Captive insurance takes risk pooling a step further by establishing an in-house insurance entity. This captive insurer is wholly owned and controlled by the insured business, providing more control over the coverage terms, premium rates, and claims process. Captive insurance allows businesses to tailor insurance programs to their specific needs, providing coverage for risks that may be underserved by the traditional insurance market.
When it comes to cyber risks, designated cyber security insurance coverage such as privacy liability coverage and network business interruption coverage play a crucial role. Privacy liability coverage protects against liabilities arising from the unauthorized access, use, or disclosure of sensitive customer data. Network business interruption coverage, on the other hand, provides coverage for financial losses resulting from cyber incidents that disrupt business operations.
Integrating designated cyber security insurance coverage with a captive insurance arrangement can be beneficial. By utilizing a captive insurer, businesses can customize their coverage to specifically address cyber risks and ensure that the policy aligns with their unique risk profile. This allows for greater flexibility and responsiveness in managing cyber threats. Additionally, captive insurance can provide businesses with more control over the claims process, leading to potentially faster and smoother claims resolution.
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, security incidents and data breaches have unfortunately become the new norm. The ever-evolving threat landscape, sophisticated cybercriminals, and the increasing reliance on technology have contributed to the rise in these incidents. Organizations across various industries are facing a constant battle to protect their valuable assets and sensitive information. The frequency and scale of security incidents and data breaches highlight the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures and proactive risk management strategies. Businesses must prioritize investments in cybersecurity infrastructure, employee awareness and training, incident response plans, and data protection practices to mitigate the risks. Collaboration and information sharing among industry peers, regulatory bodies, and cybersecurity professionals are crucial in staying ahead of emerging threats. While achieving absolute security may be challenging, organizations must continuously adapt and strengthen their defenses to minimize the impact of security incidents and data breaches, safeguard customer trust, and ensure the longevity of their operations in the increasingly digital world.
Want to know more? Get in touch with us to learn more about Captive Insurance and other ways to mitigate risks and ensure a stable future for your business.

